When you create your first website, you can encounter a lot of unknown terms. It can be so frustrating not knowing what to do and spending hours figuring out.
Today, we’ll talk about URL slugs, how to edit them in WordPress and what mistakes you should avoid making when creating slugs. For the curious minds, we’ll explain the basic parts of a URL further down below.
Ready to learn about slugs and URL structure for SEO?

Reading time: 11 minutes
What is a slug?
A slug explains the content of a web page in a few words separated by hyphens. It should be easy to read and as short as possible for users to quickly understand a page’s topic. A slug is located at the end of a URL and may be followed by a trailing slash or some parameters.
For example, “this-is-a-slug” is the URL slug in https://domain.com/this-is-a-slug/
URL slugs are editable in web CMS (Content Management Systems) like WordPress, Joomla, Wix or Squarespace.
It’s important to pick the right slug from the start to avoid SEO or link issues in the future. You’ll find some key best practices when creating URL slugs below.
How to change a URL slug in WordPress
By default, WordPress uses your post’s title as the URL slug. It works the same for pages, categories, subfolders, etc. Punctuation marks and spaces are automatically replaced by hyphens, and words are written in lowercase.
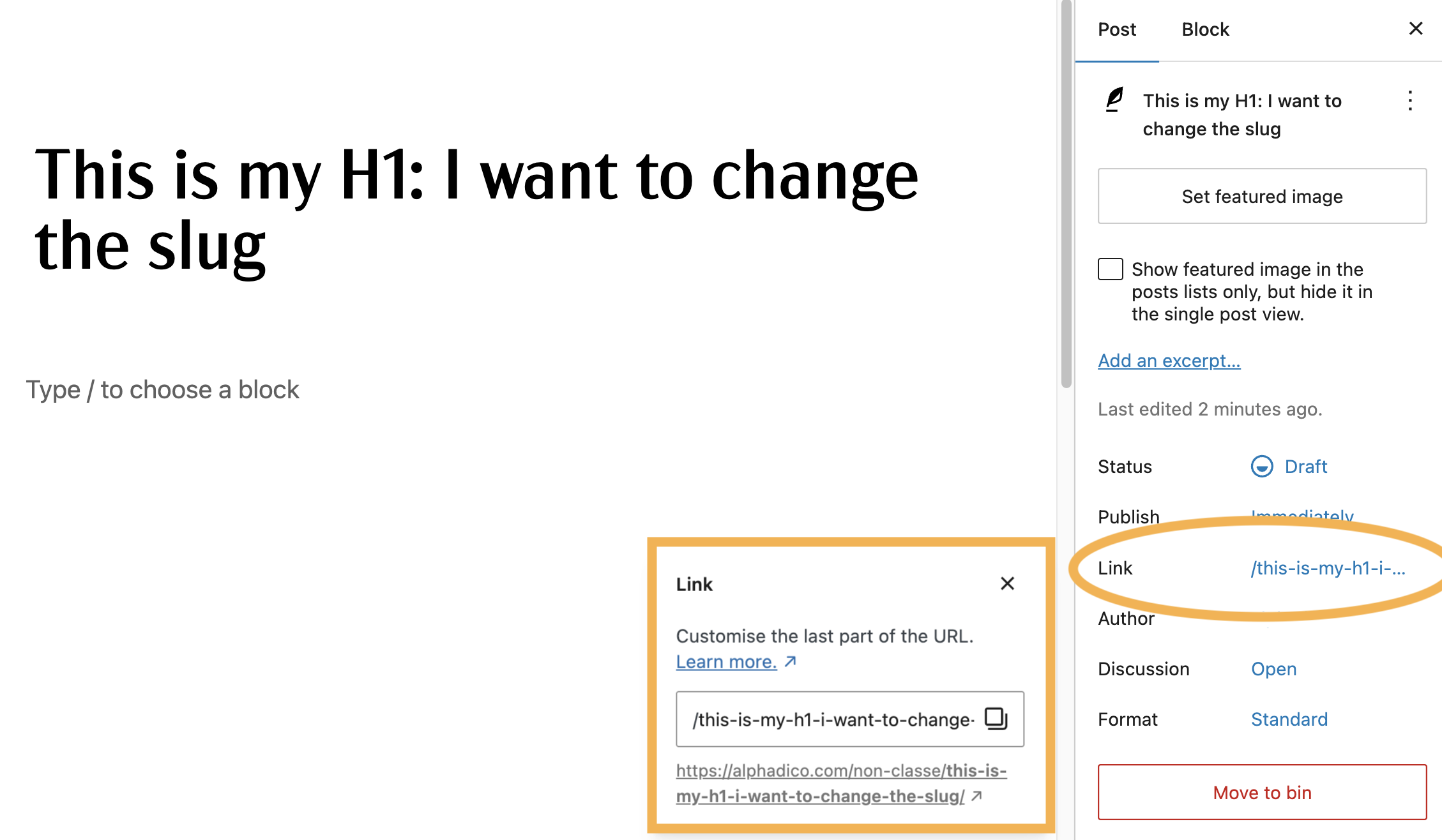
In this example, the H1 title is “This is my H1: I want to change the slug”. WordPress automatically created a slug from the title: /this-is-my-h1-i-want-to-change-the-slug.
Notice that all the words are in lowercase (“This” is now “this”), spaces and punctuation marks have been replaced by hyphens (“:” is now “-“).
If you want to edit a WordPress slug without using any SEO tools, such as Yoast or Rank Math, follow the steps below. You’ll see, it’s quick and easy!
- When editing your post (or page), click on the post’s title.
- Search for Link on the right side bar.
- Click the link to edit the WordPress slug.
- Save your post.
Do you use Yoast for your WordPress website? Here is where to change a slug with Yoast.
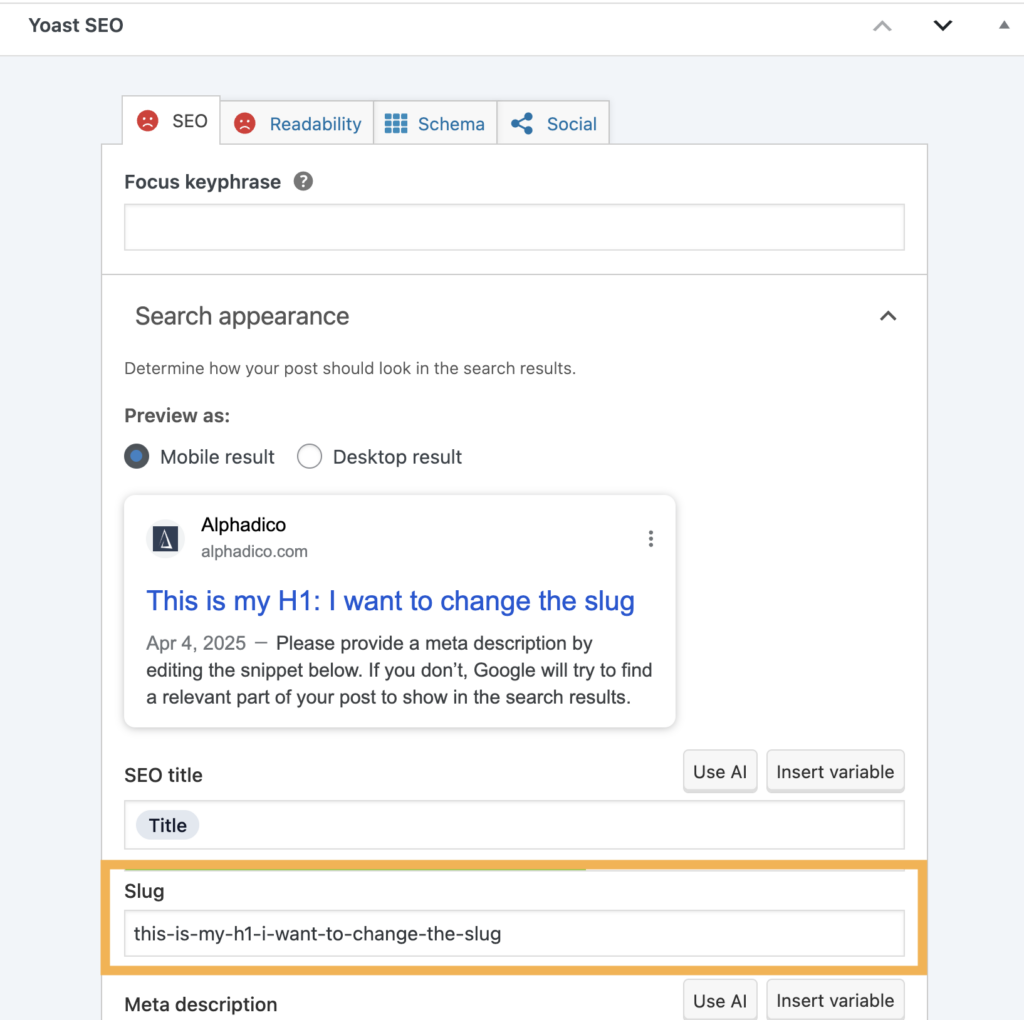
Note that, with Yoast, URL slugs only appear after saving a draft.
Make sure to follow our best practices when editing your WordPress slug.
If you wish to change a URL slug after publishing a page or a post, make sure to update the URL on all the internal and external backlinks afterwards. You can also create 301 redirects. When creating redirects, avoid loops: it could impact your SEO, slow down your website or ruin the UX (User Experience).
Best practices when creating URL slugs
When creating URL slugs, it’s crucial that you follow the best practices below. Otherwise, users might encounter 404 pages when visiting your website. Or worse, they might never find your website.
As you may know, fixing errors often takes more time than doing it right from the start. Save yourself from spending long hours changing slugs and updating URLs, read the guidelines below and create SEO-friendly slugs.
- 1. Include your main keyword in the URL slug.
- 2. Leave unnecessary stop words out.
- 3. Keep it short yet descriptive.
- 4. Use lowercase.
- 5. Make it clear and permanent.
- 6. Use hyphens, not underscores.
- 7. Avoid special characters.
- 8. Localise your slug.
1. Include your main keyword in the URL slug
Insert your main keyword in the URL slug so users have a clear idea of the topic of the page they are visiting when seeing your URL. Don’t use confusing random numbers, for example.
Slugs don’t play a big role in SEO and ranking performance, but they give key information to users and search engines. They also help increase CTR.
Which URL would you click on?
❌ /topic-2247
✅ /how-to-write-great-stories
2. Leave unnecessary stop words out
Small words such as “the”, “a” and “and” should be ignored if not clarifying what your page is about. To create SEO-friendly URL slugs, leave stop words out.
❌ /the-best-ways-to-optimise-slugs-for-beginners-and-pros
✅ /best-ways-to-optimise-slugs
3. Keep it short yet descriptive
Don’t try to add as many keywords as possible in a URL slug. Don’t use the full name of your title either, if you can create a shorter version of the slug. Instead, keep your slug short so users know straight away what your content is about and if it might be of interest to them.
❌ /how-to-write-great-slugs-and-mistakes-to-avoid-when-creating-them
✅ /how-to-write-great-slugs
4. Use lowercase
Search engines like Google might consider some of your pages as duplicates if you mix upper and lower case text elements. Only use lowercase letters in URL slugs.
❌ /SEO-Is-Fun
✅ /seo-is-fun
5. Make it clear and permanent
Avoid mentioning dates in slugs so you don’t have to use redirects in the future. Also, users may be reluctant to read your content if you forget to change the date…
❌ /how-to-write-posts-in-2023
✅ /how-to-write-posts
Only use dates in URLs if it’s relevant. Example: /key-events-2010 would be a perfect slug to describe a page listing key events that happened in 2010.
6. Use hyphens, not underscores
Separate words with hyphens (-) to make slugs understandable. Don’t join words together either.
❌ /howtousewordpress
✅ /how-to-use-wordpress
7. Avoid special characters
Forget emojis or any other non-ASCII characters. Use UTF-8 encoding if necessary.
❌ /we-are-🤓
✅ /we-are-nerds
ASCII stands for American Standard Code for Information Interchange.
UTF-8 stands for Unicode Transformation Format-8.
8. Localise your slug
If you own a multilingual website, make sure to use terms written in your audience’s language. If your audience types French words on search engines, use French words in your URL slug. Don’t mix English and French, for example.
❌ /ou-sortir-in-paris
✅ /ou-sortir-a-paris
Remember: no special characters!
❌ /où-sortir-à-paris
✅ /ou-sortir-a-paris
URL structure for SEO
Now that you know what a slug is and how to optimise it for SEO and UX, let’s talk about the structure of a URL. If you are looking to improve your ranking on SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages) and to increase traffic on your website, understanding the structure of a URL is essential.
SEO-friendly URLs allow web crawlers and users to understand the topic of a web page in the blink of an eye. That’s where permalink structure plays an important role.
What is a permalink? How to change its structure in WordPress?
Join our newsletter to find out!
You’ll then be able to choose the best URL structure for your website after discovering our setting recommendations and understanding how permalinks work.
What’s better than some URL structure examples to understand how it works?
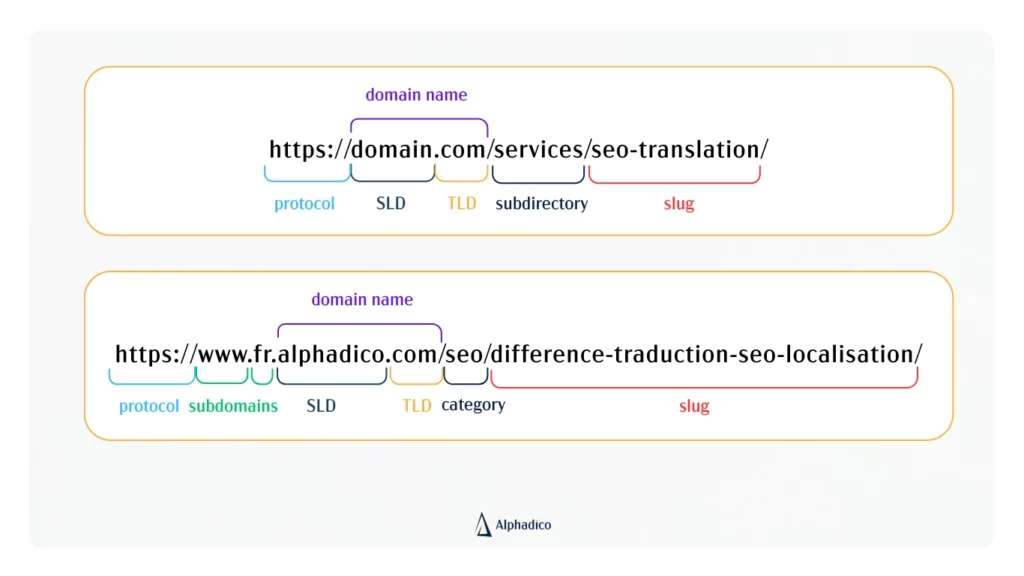
In general, URLs include:
- A protocol/scheme.
- A subdomain.
- A domain name.
- A Second-Level Domain (SLD).
- A Top-Level Domain (TLD).
- A type of subdirectory.
- A slug.
Are you wondering what these URL parts mean? Continue to read…
Protocol or scheme
The protocol, also called scheme, indicates which protocol web servers should use when accessing your website. The most common protocol for websites is HTTPS, which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure.
We highly encourage you to use HTTPS over HTTP for security reasons and for your SEO performance.
HTTPS is a ranking signal for Google and for other search engines such as Microsoft Bing, DuckDuckGo and Yahoo!.
Protocol examples: DNS, SMTP, IP, FTP, FTPS.
Subdomain
A subdomain is a specific section of a website. It indicates which particular category will be served to the users. If users visit a “blog.” subdomain, they know straight away that blog posts will be served as the main content.
Think about your wardrobe: each category of clothes is stored in its own compartment (socks, T-shirts, trousers, sweaters, etc.). A subdomain works like a compartment.
The most common subdomain is “www.” which stands for World Wide Web. Nowadays, browsers don’t always display the “www.” subdomain in URLs because it’s not that relevant any more. Also, it’s easier to remember the shorter version of a URL.
As you may have noticed in the second URL structure example, it’s possible to have several subdomains within a URL: https://www.fr.alphadico.com/seo/difference-traduction-seo-localisation/ In this example, the subdomains are “www.” and “fr.”.
Subdomain examples: news., forum., help., m., shop..
Domain name
A domain name includes a Second-Level Domain (SLD) and a Top-Level Domain (TLD). The domain name represents the name of the website. For example, alphadico.com for our website.
SLDs often refer to brands’ name while TLDs indicate which type of entity is registered under the domain name or where the domain is based. When a TLD corresponds to a country code, we use the term ccTLD. ccTLD stands for Country Code Top-Level Domain.
Examples of TLDs: .com (commercial), .gov (government), .net (network), .edu (education), .org (organisation), .info (information).
Examples of ccTLDs: .ie (Ireland), .uk (United Kingdom), .us (United States), .ca (Canada), .fr (France), .es (Spain).
Subdirectory
A subdirectory, also called a subfolder, helps compartment a website into folders –or into categories. A subdirectory is similar to a subdomain, except that it’s a subsection of the subdomain.
For example, “shoes” is the subdirectory of the subdomain “shop.” in the following URL: https://shop.brand.com/shoes/black-shoes/
Other example: “marketing” is the subdirectory of the URL below.
https://domain.com/marketing/tips-for-your-seo/
Slug
As mentioned previously, a slug explains the content of a web page and is located at the end of a URL.
The URL slug of this article is “url-structure-explained-slug-definition”. When you read it, you understand that the article will explain the structure of a URL and will give the definition of a slug. The tips and slug guidelines shared in the article are a bonus for readers who are interested in SEO best practices for URL slugs. We could have included this information in the slug, but we decided not to. We like to keep our slugs concise (2 to 5 words on average).
Conclusion
To avoid penalising your ranking or your SEO performance, make sure you understand basic URL structures. Also, follow the 8 best practices for slug creation we shared with you to avoid editing URL slugs in the future and risking broken links. Your goal is to share relevant content with your website visitors, and not to send them towards 404 error pages.
Follow our guidelines and make it right from the start!


